Categories
- Iridology Software FQA (4)
- Iridology Iris Diagnosis (2)
- Iridology (39)
- Case Analysis (0)
- BLOG (29)
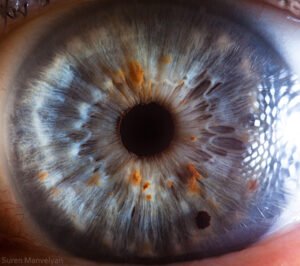
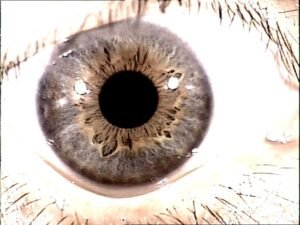
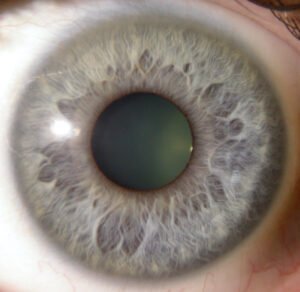
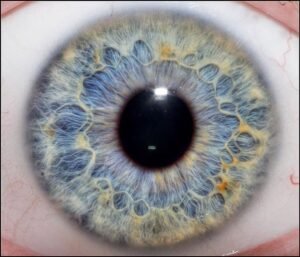
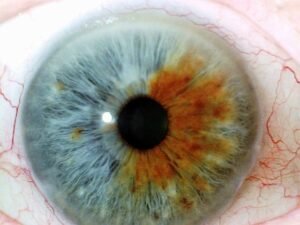
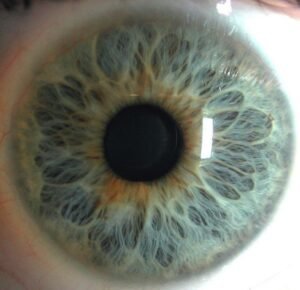
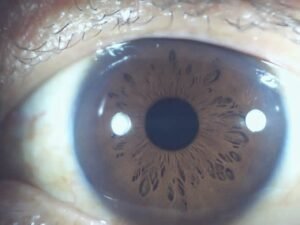
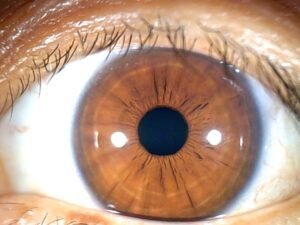
color Iridology plays significant role in iridology, can reveal various aspects individual’s health and genetic makeup. Initially, human irises were categorized into two primary colors: blue and brown. Over time, due to genetic diversity and intermarriage, more variations in Iridology colors have emerged, and now there approximately dozen different eye colors.
basic color Iridology, well any secondary colors or deposits that might appear in Iridology, crucial in understande overall health. These colors may be inherited, but can also change throughout life based on factors like environmental exposure, lifestyle choices, and medical conditions. In iridology, each variation in color is often linked to different health conditions or tendencies.
| Iridology Color | Description | Health Implications |
|---|---|---|
| Brown | Brown eyes contain high amounts melanin, give them darker hue. | Brown eyes associated with stronger immune systems and more resilience against environmental stressors. However, may also indicate tendency toward inflammatory conditions. |
| Blue | Blue eyes have less melanin and lighter appearance. | Individuals with blue eyes may be more prone to conditions like light sensitivity or autoimmune diseases due to lower melanin levels. can also indicate genetic weaknesses in certain areas. |
| Gray | A gray Iridology tends to be lighter shade blue but with subtle gray hues. | A gray Iridology can suggest sensitive and nervous system, with higher likelihood stress-related conditions, especially when t pronounced gray-blue hue. |
| Green | Green eyes contain mixture melanin and other pigmentary deposits that create distinct green hue. | Green eyes often linked with higher likelihood hormonal imbalances and liver issues, well energetic, passionate personality. |
| Hazel | Hazel eyes combination brown and green tones, give them multi-colored appearance. | Hazel-eyed individuals may be prone to digestive issues or liver conditions, depende on hue and intensity green or brown mix. |
| Amber | Amber eyes have golden-yellow tint, which comes from presence specific pigment called lipochrome. | People with amber eyes may have higher chance experience cardiovascular or respiratory issues, well tendency emotional sensitivity. |
| Light Blue / Light Grey | A very pale blue or grayish Iridology, often due to low pigmentation. | This color could indicate sensitivity to light and more delicate constitution, with greater susceptibility to stress, inflammation, and autoimmune conditions. |
| Black | Very dark eyes, which sometimes appear black due to high concentration melanin. | Black irises linked to strong constitution but can also indicate higher likelihood digestive issues or liver toxicity, depende on individual. |
| Yellow or Orange | Occurs when there is accumulation metabolic waste products or toxins in Iridology, often seen in form streaks or spots. | Yellow or orange coloration often suggests liver or kidney dysfunction, poor detoxification processes, or dietary imbalances, these organs struggle to process toxins. |
| Factor | Impact on Iridology Color |
|---|---|
| Genetic Inheritance | basic color your Iridology is primarily determined by genes inherited from your parents. |
| Health Conditions | Illnesses, particularly those affecte liver, kidneys, or digestive system, can lead to visible changes in Iridology color. |
| Lifestyle Choices | Diet, exercise, exposure to toxins, and stress can all alter pigment levels and overall appearance Iridology. |
| Medications | Certain drugs and medications can cause pigment deposits in Iridology, change its color. |
| Age | we age, pigment in Iridology may degrade or change, leade to shifts in Iridology color or appearance new discolorations. |
Dark Iridology (Brown/Black): People with darker eyes tend to have more melanin, which gives them greater protection from UV light and oxidative damage. However, may be more prone to inflammatory conditions or internal stress due to more reactive immune system.
Light Iridology (Blue/Gray): Lighter irises typically indicate lower levels melanin and might be linked to more sensitive immune system. These individuals may experience more external environmental sensitivities, such allergic reactions or autoimmune tendencies. also more susceptible to UV damage and eye strain.
Mixed Iridology (Hazel, Green): combination different colors, such hazel or green, reflects balance internal and external influences on Iridology. These individuals may have predisposition to both genetic and lifestyle-related health issues.
Dr. Bernard Jensen (Iridology Pioneer):
” color Iridology is more than just reflection beauty; is window into soul and health body. various hues, spots, and patterns found in Iridology provide us with profound insight into state person’s internal organs and systems.”
Dr. Peter Thiel (German Iridologist):
“Iridology allows us to connect dots between genetic predispositions and lifestyle impacts. color Iridology is important piece this puzzle, helps indicate potential weaknesses or strengths in person’s health.”
Dr. Henry Edward Lane (Founder Iridology in U.S.):
“When we examine Iridology and its color, we uncover not only genetic traits but also potential concern that could be addressed before become serious health issues. Iridology color is crucial diagnostic tool in preventive health care.”
In summary, color Iridology plays significant role in iridology and offers important clues about individual’s overall health, genetic predispositions, and potential health risks. By examine color variations, iridologists can gain insight into underlye conditions and help guide preventative care.
